Surgical Skill Prediction
Improving surgical skill prediction on unsupervised simulated JIGSAWS dataset.
Segmentation of surgical tools is a supervised method and requires heavy human labor in the form of annotation of the videos. Also, there is a scarcity of availability of open clinical datasets. To mitigate the dependency on clinical data and manual evaluation of surgical skill, we propose a modified unsupervised segmentation method and implement it on the JIGSAWS dataset. The segmentation method makes use of visual cues like optical flow, color and location and uses them as pseudo labels. These pseudo labels are then used to train a model to perform segmentation of the surgical instruments. The segmentation masks generated are then used as input to the surgical skill assessment model, which predicts the skill level of a surgery.
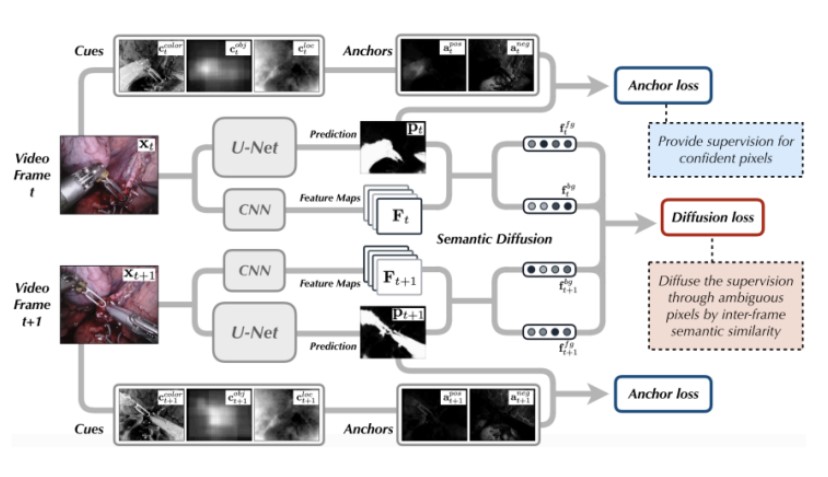
For Unsupervised Tool Segmentation, we uses handcrafted cues to generate pseudo labels. These cues include optical flow, color and location. Cues are probability maps that help us detect the presence of a surgical tool at a given pixel. After generating the three cues for each image, the element-wise multiplication of these cues give us anchors. These anchors are aggregated with the output of a U-Net to provide the anchor loss. To capture inter-frame semantic similarity, predictions from the U-Net and the output feature maps of a pre-trained CNN are aggregated to generate a diffusion loss. The goal of the unsupervised segmentation model is then to optimize the combined loss.
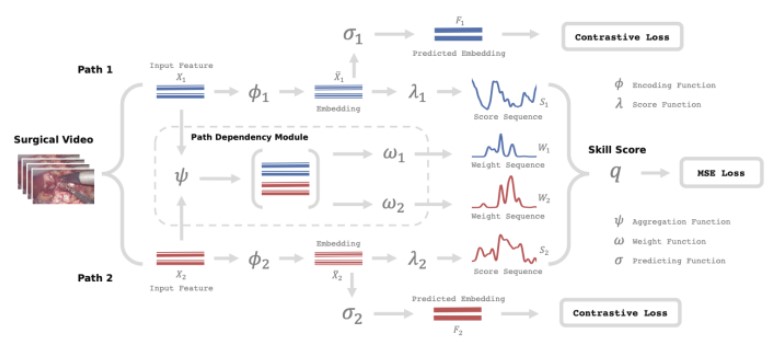
The segmentation masks are then passed as input to the multi-path Unified Skill Prediction Model for predicting how well a surgery is performed. This model proposes a unified multi-path framework for surgical skill assessment, which takes care of multiple aspects of surgical skills which include surgical tool usage, intraoperative event pattern, and other skill proxies. The dependencies among these aspects are modified by a path dependency module. Following are the three aspects considered in the model:
- Movement of surgical tools - helps capture the tool handling proficiency of the surgeon.
- Clearness of the operating field as a skill proxy - A clear operating field ensures high visibility of anatomy structures, which is critical for the surgeon’s performance.
- Workflow of surgical events - evaluates if the surgery was performed in an orderly manner necessary for a well performed surgery.
The path dependency module then captures the inter-dependencies between these paths giving an overall surgery score.